Stock Market Mastery The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide

Stock Market
Introduction
The stock market plays a crucial role in economic development by enabling companies to raise capital and providing individuals with opportunities to grow wealth. This comprehensive guide covers the fundamentals of the stock market, how it operates, key participants, types of stocks, investment strategies, and potential risks.
It also delves into stock market indices, the role of technology in trading, and future trends that could shape market dynamics. Whether you are a beginner looking to make your first investment or an experienced trader seeking new insights, this blog offers valuable knowledge to help you navigate the stock market with confidence.
Learn how to analyze stocks, manage risks, and develop strategies that align with your financial goals. Stay ahead of market trends and make informed investment decisions with this in-depth 2500-word guide on the stock market.
The Stock Market: A Comprehensive Guide

Stock Market
The stock market is a crucial component of the global financial system, enabling companies to raise capital and investors to participate in corporate success. It has played a significant role in economic development and wealth creation for centuries. This blog explores the fundamentals of the stock market, its functioning, key participants, investment strategies, risks involved, and future trends. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced investor, understanding the stock market can help you make informed financial decisions and grow your wealth over time.
What is the Stock Market?
The stock market refers to the collection of exchanges and platforms where stocks (shares of ownership in companies) are bought and sold. It is an essential aspect of capitalism, allowing businesses to raise funds and individuals to invest in enterprises. The market is divided into primary and secondary markets.
- The primary market involves the issuance of new shares through Initial Public Offerings (IPOs), where companies offer their stock to the public for the first time.
- The secondary market involves the buying and selling of these stocks among investors on exchanges such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), Nasdaq, and London Stock Exchange (LSE).
Stock prices fluctuate based on supply and demand, company performance, economic indicators, and market sentiment. When investors believe a company has growth potential, demand for its stock increases, pushing its price higher. Conversely, negative news can lead to stock sell-offs, causing a price decline.
The Importance of the Stock Market
The stock market plays a crucial role in the economy by facilitating capital formation, economic growth, and wealth accumulation. It offers businesses access to funding, enables investors to grow their capital, and provides a benchmark for economic performance. Governments and financial institutions monitor stock market performance to gauge economic health and formulate policies accordingly.
Key Participants in the Stock Market
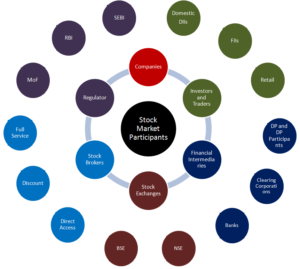
Stock Market
- Investors – Individuals or institutions that buy and sell stocks. These can be retail investors, who invest their personal funds, or institutional investors, including hedge funds, pension funds, and mutual funds.
- Traders – Engage in short-term buying and selling to capitalize on market fluctuations. Traders use various strategies such as day trading, swing trading, and scalping.
- Stockbrokers – Licensed professionals who facilitate trades for investors. They earn commissions on transactions and provide investment advice.
- Market Makers – Ensure liquidity by buying and selling stocks to provide a smooth trading process. Their role is crucial in preventing large price swings due to supply-demand imbalances.
- Regulators – Organizations like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) oversee market activities to maintain transparency and fairness. Other regulatory bodies include the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) and international equivalents such as SEBI in India.
Types of Stocks
Stocks can be broadly categorized into:
- Common Stocks – Represent ownership in a company with voting rights and potential dividends. Investors benefit from capital appreciation and dividend payments.
- Preferred Stocks – Offer fixed dividends but generally lack voting rights. These stocks are preferred in terms of dividend payments but do not provide ownership benefits like common stocks.
- Growth Stocks – Companies expected to grow at an above-average rate. Investors buy these stocks with the hope of future price appreciation.
- Value Stocks – Shares trading at lower valuations relative to their intrinsic worth. These stocks are considered undervalued based on financial ratios like Price-to-Earnings (P/E) and Price-to-Book (P/B) ratios.
- Dividend Stocks – Provide regular income through dividends. Investors favor these stocks for stability and income generation.
Stock Market Indices
Stock Market
Stock indices measure the performance of specific market segments and help investors gauge overall market health. Examples include:
- S&P 500 – Tracks 500 large U.S. companies.
- Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) – Comprises 30 major industrial stocks.
- Nasdaq Composite – Includes technology and growth-oriented stocks.
- Nifty 50 & Sensex – Represent Indian stock market performance.
How to Invest in the Stock Market
- Open a Brokerage Account – Select a reliable brokerage firm and create an investment account.
- Research and Choose Stocks – Analyze financial reports, market trends, and company fundamentals.
- Diversify Your Portfolio – Spread investments across different sectors to minimize risk.
- Monitor Investments – Keep track of market movements and adjust holdings accordingly.
- Long-term vs. Short-term Strategy – Decide whether to invest for the long haul or trade actively.
Fundamental and Technical Analysis
Fundamental Analysis involves evaluating a company’s financial health, including earnings, assets, liabilities, and market position. Metrics such as the Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio, Return on Equity (ROE), and revenue growth are critical.
Technical Analysis uses charts, patterns, and statistical indicators to predict future price movements. Common tools include moving averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Bollinger Bands.
Risks in the Stock Market
Investing in stocks carries various risks, including:
- Market Risk – Overall market fluctuations affecting stock prices.
- Company Risk – Poor financial performance or management failures.
- Economic Risk – Inflation, interest rates, and economic downturns.
- Liquidity Risk – Difficulty in selling stocks at desired prices.
- Political and Regulatory Risks – Government policies impacting investments.
Investment Strategies
- Buy and Hold – Long-term investment strategy focused on value appreciation.
- Value Investing – Buying undervalued stocks and holding them until they reach their potential.
- Growth Investing – Investing in companies with high growth prospects.
- Dividend Investing – Focusing on stocks that provide regular dividends.
- Day Trading – Buying and selling stocks within the same trading day.
Future Trends in the Stock Market
- ESG Investing – Focus on Environmental, Social, and Governance factors.
- Cryptocurrency and Blockchain – Integration of digital assets with traditional markets.
- Artificial Intelligence in Trading – AI-driven market predictions and automated trading.
Conclusion
The stock market offers numerous opportunities for wealth creation but requires careful planning, research, and risk management. By understanding its fundamentals and adopting a strategic approach, investors can make informed decisions and achieve their financial goals. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced investor, staying updated with market trends and continuously refining your investment strategy is key to long-term success. The stock market is not just about making quick money but building sustainable wealth over time.
Learn to More Stock Market Info
Do Check This Article Too Link
