A Comprehensive Guide to the NEET Exam

The National Eligibility cum Entrance Test (NEET) is one of the most significant medical entrance exams in India. Conducted by the National Testing Agency (NTA), serves as a gateway for students aspiring to pursue undergraduate medical (MBBS), dental (BDS), and AYUSH courses in recognized medical institutions across India. With thousands of aspirants competing every year, considered one of the most challenging entrance exams in the country.
Importance of NEET
NEET plays a crucial role in standardizing medical admissions in India. Before introduced, multiple entrance exams were conducted by states and private institutions, making the admission process complex and non-uniform.
Additionally, NEET is the only entrance exam for admission to government and private medical colleges in India, replacing exams like AIIMS and JIPMER. It also serves as an eligibility criterion for Indian students who wish to study medicine abroad.
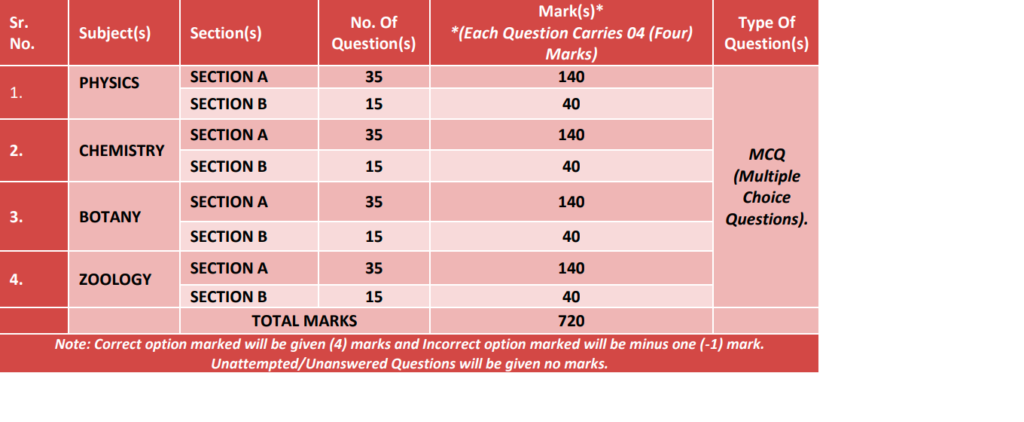
NEET Exam Pattern
Understanding the exam pattern is crucial for effective preparation. NEET is a pen-and-paper-based test consisting of a single paper with multiple-choice questions (MCQs). The exam duration is three hours, and it comprises 200 questions from three major subjects:
- Physics – 50 questions (45 to be attempted)
- Chemistry – 50 questions (45 to be attempted)
- Biology (Botany and Zoology) – 100 questions (90 to be attempted)
Each correct answer fetches four marks, while an incorrect answer results in a deduction of one mark due to negative marking. The total maximum marks for NEET are 720.
NEET Syllabus
The NEET syllabus is derived from the NCERT curriculum of classes 11 and 12. Students preparing for the exam must have a strong grasp of the following topics:
Physics:
- Motion, Laws of Motion, Work, Energy, and Power
- Thermodynamics, Electrostatics, Optics, and Modern Physics
- Current Electricity, Magnetism, and Semiconductor Devices
Chemistry:
- Physical Chemistry: Atomic Structure, Chemical Bonding, Thermodynamics, and Equilibrium
- Organic Chemistry: Basic Concepts, Hydrocarbons, Biomolecules, and Polymers
- Inorganic Chemistry: Periodic Table, Coordination Compounds, and Environmental Chemistry
Biology:
- Cell Structure, Human Physiology, Plant Physiology
- Genetics, Biotechnology, and Evolution
- Ecology, Biodiversity, and Human Health & Diseases

Preparation Strategy for NEET
1. Understand the Syllabus and Exam Pattern:
Familiarizing yourself with the syllabus and exam pattern helps in planning an effective study schedule. Prioritize high-weightage topics to maximize your score.
2. Create a Realistic Study Plan:
Divide your study time effectively, giving equal attention to all three subjects. Allocate more time to topics you find challenging and revise regularly.
3. Refer to NCERT Books:
NCERT textbooks for classes 11 and 12 are the most important resources for NEET preparation. These books provide conceptual clarity and cover almost all the topics asked in the exam.
4. Practice Mock Tests and Previous Year Papers:
Regular practice of mock tests and past question papers helps in understanding the exam pattern, improving time management, and identifying weak areas.
5. Take Regular Breaks and Stay Consistent:
Studying continuously without breaks can lead to burnout. Take short breaks between study sessions to refresh your mind and maintain consistency.
6. Seek Guidance and Join Coaching (if needed):
While self-study is crucial, joining a coaching institute or taking online courses can provide structured learning and expert guidance.

NEET Eligibility Criteria
Candidates appearing for NEET must meet the following eligibility requirements:
1. Educational Qualification
- Candidates must have completed 10+2 or equivalent from a recognized board.
- Must have studied Physics, Chemistry, Biology/Biotechnology, and English as core subjects.
- Candidates appearing for their 12th board exams in the same year as NEET can also apply, but they must provide proof of passing at the time of admission.
2. Minimum Marks Requirement in PCB (Physics, Chemistry, Biology/Biotechnology)
- General category: Minimum 50% aggregate marks in PCB.
- OBC/SC/ST categories: Minimum 40% aggregate marks in PCB.
- PwD (Persons with Disability) candidates: Minimum 45% aggregate marks in PCB (for General-PwD category).
3. Age Limit
- Minimum Age: Candidates must be at least 17 years old as of December 31 of the exam year.
- Upper Age Limit: No upper age limit, as per the latest guidelines.
4. Nationality Criteria
Candidates can be:
- Indian Nationals
- Non-Resident Indians (NRIs)
- Overseas Citizen of India (OCI)
- Persons with Indian Origin (PIO)
- Foreign Nationals (eligible for admission under specific quotas)
5. Number of Attempts
- There is no restriction on the number of attempts. Candidates can appear for NEET as many times as they meet the eligibility criteria.
6. NEET Qualification for Studying Abroad
- Indian students planning to study MBBS abroad must qualify for NEET to obtain the Eligibility Certificate from the National Medical Commission (NMC).
7. State Quota & AIQ (All India Quota) Eligibility
- 85% State Quota: Candidates must fulfill domicile requirements for their respective states to be eligible for state medical colleges.
- 15% All India Quota (AIQ): All candidates are eligible, except for those from Jammu & Kashmir, unless they opt for AIQ during application.
8. Additional Requirements for Foreign Nationals
- Must provide proof of passing 10+2 equivalent examination with the required subjects.
- Should verify specific medical college admission criteria, as some institutions may have additional eligibility conditions.
NEET Cut-Off and Admission Process
The NEET cut-off varies each year based on factors like exam difficulty and the number of candidates appearing. The cut-off marks are divided into categories:
- General Category: Around 50th percentile
- OBC/SC/ST Categories: Around 40th percentile
- PwD Category: Around 45th percentile
After the exam, qualifying candidates participate in the All India Quota (AIQ) and State Quota counseling processes for seat allotment in medical colleges.
Conclusion
NEET (National Eligibility cum Entrance Test) is the gateway to fulfilling the dream of becoming a doctor. It is one of the most competitive medical entrance exams in India, requiring dedication, strategic planning, and disciplined preparation. With the right strategy, perseverance, and a focused mindset, aspirants can overcome challenges and achieve their goals.
Success in NEET is not just about intelligence—it’s about consistent effort, time management, and smart study techniques. Understanding concepts thoroughly, practicing regularly, and maintaining a positive attitude are crucial. A well-structured study plan, combined with mock tests, revision, and self-analysis, helps students stay on track and improve their performance.
The journey to cracking NEET may be demanding, but it is also rewarding. Every hour spent studying, every test attempted, and every concept mastered brings an aspirant closer to their dream of wearing the white coat and serving humanity. Staying motivated, avoiding distractions, and keeping a healthy balance between studies and relaxation can make the process smoother and more effective.
For those who remain determined, resilient, and passionate, the dream of entering the medical field becomes a reality. The path to becoming a doctor may be tough, but with unwavering dedication and a never-give-up attitude, a bright future in the medical profession awaits.

